Hey
I am currently working on a project in Arduino for school, with Blynk. I use the app for Android.
This is my first project in Arduino / Blynk. The code is not yet optimal, but it works. Or at least partly.
I control 2 servo motors via inverse kinematics. I’m using an Arduino Mega + Ethernet Shield.
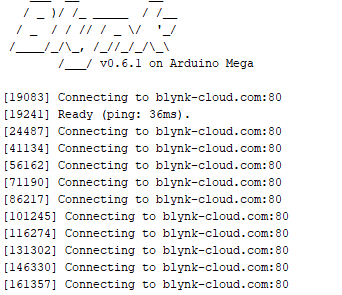
I use a joystick (V15 -> x and V16 -> y). If I move the joystick once, the program freezes.
I’ve already tried using sliders (only as a test), but that also has the same result. The joystick is set to 1 second. Merge / split also provide the same result. I’ve been searching for a while, hope you can tell me where it goes wrong.
I don’t use the timer to write data back to the app. I use a delay. So that data is certainly not exchanged more than 10 times per second. (see delay for ExportData).
Thanks in advance!
// Bibliotheken
#include <SPI.h> // Communicatie tussen Arduino en SD-kaart
#include <Ethernet.h> // Ethernetbibliotheek
#include <BlynkSimpleEthernet.h> // Blynkethernetbibliotheek
#include <Servo.h> // Servobibliotheek
// Constanten
const float d12 = 42;
const float d13 = 80;
const float d24 = 80;
const float d35 = 100;
const float d45 = 100;
const float d56 = 20;
const float y1 = 0;
const float y2 = 0;
const float a456 = 2.094395;
const int L_laag = 600; // Servo_L onderlimiet
const int L_hoog = 2000; // Servo_L bovenlimiet
const int R_laag = 900; // Servo_R onderliemiet
const int R_hoog = 2400; //Servo_R bovenlimiet
// Variabelen
float x = 0;
float y = 100;
float d46;
float a465;
float d26x;
float d26y;
float alfa2;
float d26;
float a426;
float theta2 = 2123.78; // Initiële stand Servo_R
float a264;
float alfa5;
float x5;
float y5;
float d15x;
float d15y;
float alfa1;
float d15;
float a315;
float theta1 = 901.99; // Initiële stand Servo_L
const float pi = M_PI; // Opslaan van Pi in een handig formaat
float theta1_old = 901.99; // Vergelijkingsvariabele voor theta 1
float theta2_old = 2123.78; // Vergelijkingsvariabele voor theta 2
float x_old = 0; // Vergelijkingsvariabele voor X
float y_old = 100; // Vergelijkingsvariabele voor Y
// Servomotoren
Servo Servo_L; // Servomotor Links
Servo Servo_R; // Servomotor Rechts
// Connecties
#define SERVO_L_PIN 40 // SERVO_L_PIN koppelen aan pin 40
#define SERVO_R_PIN 41 // SERVO_R_PIN koppelen aan pin 41
// Noodzakelijke connecties Blynk:
#define BLYNK_DEBUG
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
char auth[] = "ZlwrQh0809oBgdHZRqg57tKeMJ7n1ZnV";
#define W5100_CS 10
#define SDCARD_CS 4
WidgetTerminal terminal(V12);
BLYNK_WRITE(V15){ // Import coördinaten via Blynk na push in app
x = param.asFloat(); // Input nieuwe X via Blynk
terminal.print("Nieuwe X: ");
terminal.println(x);
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V16){ // Import coördinaten via Blynk na push in app
y = param.asFloat(); // Input nieuwe Y via Blynk
terminal.print("Nieuwe Y: ");
terminal.println(y);
}
// Limieten
float servoLimit (float micros_in, float micros_min, float micros_max) { // Wordt uitgevoerd in subprogramma: Output
if (micros_in > micros_max) micros_in = micros_max; // Indien waarde lager dan onderlimiet: gebruik onderlimiet
if (micros_in < micros_min) micros_in = micros_min; // Indien waarde hoger dan bovenlimiet: gebruik bovenlimiet
return micros_in; // Teruggeven van de correcte waarde
}
// Setup (éénmalige uitvoering van code)
void setup()
{
Serial.println("Uitvoeren Setup");
// Servomotoren koppelen aan de correcte uitgangen
Servo_L.attach(SERVO_L_PIN); // Servo_L koppelen met SERVO_L_PIN
Servo_R.attach(SERVO_R_PIN); // Servo_R koppelen met SERVO_R_PIN
// Seriële monitor activeren
Serial.begin(9600); // Baudrate van seriële monitor vastleggen
while (!Serial); // Wachten tot de seriële poort geconecteerd is
//Servomotoren in startpositie plaatsen
Servo_L.write(theta1); // Servo_L plaatsen in positie theta 1
Servo_R.write(theta2); // Servo_R plaatsin in positie theta 2
// Uitschakelen SD-kaart
pinMode(4, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(4, HIGH);
// Authenticatie Blynck uitvoeren
Blynk.begin(auth);
}
/* ******************************************************************************
HOOFDPROGRAMMA
*/
void loop()
{
Blynk.run(); // Uitvoeren Blynk
InverseKinematica(); // Uitvoeren subprogramma: Inverse kinematica
Output(); // Uitvoeren subprogramma: Controle + aansturen
delay(200); // Vertraging
ExportData(); // Uitvoeren subprogramma: ExportData (naar Blynk)
}
/* ******************************************************************************
SUBPROGRAMMA'S
*/
// SUB: Inverse kinematica
void InverseKinematica()
{
d46 = sqrt( sq(d45) + sq(d56) - 2 * d45 * d56 * cos(a456) );
a465 = acos( (sq(d45) - sq(d46) - sq(d56)) / (-2 * d46 * d56) );
d26x = x - (d12 / 2);
d26y = y - y2;
alfa2 = atan2(d26y, d26x);
d26 = sqrt( sq(d26x) + sq(d26y) );
a426 = acos( (sq(d24) + sq(d26) - sq(d46)) / (2 * d24 * d26) );
theta2 = alfa2 - a426;
a426 = acos( (sq(d24) + sq(d26) - sq(d46)) / (2 * d24 * d26) );
theta2 = R_hoog - 10 * ( ((alfa2 - a426) * 4068) / 71);
a264 = acos( (sq(d46) + sq(d26) - sq(d24)) / (2 * d46 * d26) );
alfa5 = alfa2 + pi + a264 - a465;
x5 = d56 * cos(alfa5) + x;
y5 = d56 * sin(alfa5) + y;
d15x = (-d12 / 2) - x5;
d15y = y5 - y1;
alfa1 = atan2(d15y, d15x);
d15 = sqrt( sq(d15x) + sq(d15y) );
a315 = acos( (sq(d13) + sq(d15) - sq(d35)) / (2 * d13 * d15) );
theta1 = 10 * ( ((alfa1 - a315) * 4068) / 71) + L_laag;
}
// SUB: Output
void Output()
{
// Controle van de limieten
theta1 = servoLimit(theta1, L_laag, L_hoog); // Controle op limeiten Theta 1
theta2 = servoLimit(theta2, R_laag, R_hoog); // Controle op limeiten Theta 2
Servo_L.write(theta1); // Aansturen motor Links (theta 1)
Servo_R.write(theta2); // Aansturen motor Rechts (theta 2)
// Uitschrijven gegevens naar seriële poort
if (theta1 != theta1_old) { // Indien theta 1 wijzigt, dan..
Serial.print("Theta 1 naar: ");
Serial.println(theta1);
theta1_old = theta1; // Verangen oude theta 1 door nieuwe theta 1
}
// Aansturen servo rechts + uitschrijven hoek
if (theta2 != theta2_old) { // Indien theta 2 wijzigt, dan..
Serial.print("Theta 2 naar: ");
Serial.println(theta2);
theta2_old = theta2; // Vervangen oude theta 2 door nieuwe theta 2
}
}
// SUB: ExportData
void ExportData()
{
terminal.println(F("Export Data."));
Blynk.virtualWrite(V0, theta1); // Sturen theta1 naar virutele pin 0
terminal.println(theta1);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, theta2); // Sturen theta2 naar virtuele pin 1
terminal.println(theta2);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, x); // Sturen x naar virtuele pin
terminal.println(x);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, y); // Sturen y naar virtuele pin 3
terminal.println(y);
}

 )
)