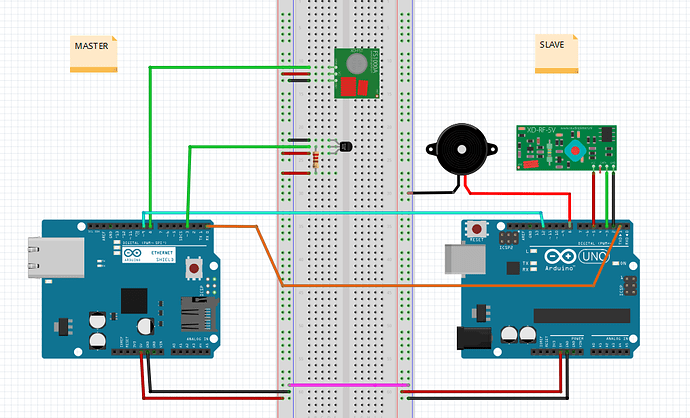
As so many other fellow Blynkers, I too want my home to be a little bit smarter than my neighbors. From the beginning I just wanted a scheduler to turn on/off my remote controlled power sockets, but during the process it evolved to also include a receiver. I can now control my sockets with both the physical remote and Blynk seamlessly – AND get the correct status in my phone.
But implementing a super regenerative receiver wasn’t without its problem due to its “no signal noise” characteristics and eventually made me go for a two MCU solution. One (called SLAVE) that’s only receiving and passing decoded signals to the main MCU (called MASTER).
Hardware used, the keyword is cheap:
- 2 x Arduino UNO. The plan was to use an ATTiny85 as SLAVE, but I had UNO’s at home so…
- 1 x W5100 Ethernet shield
- 1 x XY-MK-05 Receiver
- 1 x FS1000A Transmitter
- 1 x Piezo buzzer
- 1 x Dallas DS18B20 temperature sensor
- 1 x 4.7 Ohm resistor
- 3 x RF controlled power sockets that’s using ASK/OOK modulation on 433 Mhz.
A previous post regarding SRR and “no signal noise” problem:
My “Need Help With My Project” thread, now marked as “Solved”:
A small Fritzing to illustrate the setup:
Code for MASTER:
/**
RF433_Master.ino
Used togheter with RF433_Slave.ino
**/
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
#include <NexaSelfLearningTransmitter.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEthernet.h>
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
#include <WidgetRTC.h>
const byte W5100_CS = 10;
const byte SDCARD_CS = 4;
//============ MASTER <-> SLAVE
// MASTER Serial RX pin 0 is connected to SLAVE TX pin 1
const byte signalPin = 9; // To: SLAVE pin 12. Set to HIGH when transmitting
// Dont forget common ground!
//============ Temp sensor
const byte ONE_WIRE_BUS = 3;
OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);
DallasTemperature DS18B20(&oneWire);
bool newTemp = false;
//============ Transmitter
uint8_t TX_PIN = 8;
uint8_t TX_LED = 7; // Not connected, but need to be defined (and W5100 uses 13).
NexaSelfLearningTransmitter transmitter = NexaSelfLearningTransmitter(TX_PIN, TX_LED);
bool on = false;
bool group = false;
short dim = 0;
uint8_t channel = 0;
uint64_t receivedSignal = 0;
uint32_t TRANSMITTER_ID = 1912830;
//============ Reading serial buffer and parsing data
const byte numChars = 26; // Needs to hold something like this: <1912830,1,14,0,-1>
char receivedChars[numChars];
char tempChars[numChars];
long int pTransmitter;
int pOn;
int pGroup;
int pChannel;
int pDim;
bool newData = false;
//============ Blynkkk stuff
WidgetTerminal terminal(V4);
BlynkTimer timer;
WidgetRTC rtc;
char currentTime[9];
bool clockSync = false;
char auth[] = "";
byte arduino_mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xED, 0xBA, 0xFE, 0xFE, 0xCC };
IPAddress arduino_ip (192, 168, 0, 20);
IPAddress dns_ip (192, 168, 0, 1);
IPAddress gateway_ip (192, 168, 0, 1);
IPAddress subnet_mask(255, 255, 255, 0);
//============ Setup
void setup() {
pinMode(signalPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW); // HIGH when sending
pinMode(SDCARD_CS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SDCARD_CS, HIGH); // Deselect the SD card
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println();
DS18B20.begin();
DS18B20.setWaitForConversion(0); // See the "Temperature sensor" block below for more information
Blynk.begin(auth, "cloud.blynk.cc", 8442, arduino_ip, dns_ip, gateway_ip, subnet_mask, arduino_mac);
while (Blynk.connect() == false) {
// Wait until connected
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 24; i++) {
terminal.println(""); // "clear screen" in app.
}
terminal.flush();
terminal.println(F("Blynk v" BLYNK_VERSION ": Device started"));
terminal.println(F("-------------"));
terminal.flush();
timer.setInterval(60000L, activetoday); // check every 60s if ON / OFF trigger time has been reached
timer.setInterval(30000L, reconnectBlynk); // check every 30s if still connected to server
timer.setInterval(5000L, clockDisplay); // check every 5s if time has been obtained from the server
timer.setInterval(60000L, getSensorData); // check for new temp data every 60s
timer.setInterval(600000L, startSensorConversation); // tells the sensor to do a new conversation/reading every 10 min
timer.setInterval(1000L, readSerialBuffer); // check for new data from SLAVE in buffer every second
}
void timeStamp() {
clockSync = false;
clockDisplay();
}
BLYNK_CONNECTED() {
rtc.begin();
}
void activetoday(){ // check if schedule should run today
if(year() != 1970){
Blynk.syncVirtual(V10); // sync scheduler #1
}
}
void clockDisplay(){ // only needs to be done once after time sync
if((year() != 1970) && (clockSync == false)){
sprintf(currentTime, "%02d:%02d:%02d", hour(), minute(), second());
Serial.println(currentTime);
terminal.println(currentTime);
terminal.flush();
clockSync = true;
}
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V10) { // Scheduler #1 Time Input widget
TimeInputParam t(param);
unsigned int nowseconds = ((hour() * 3600) + (minute() * 60) + second());
unsigned int startseconds = (t.getStartHour() * 3600) + (t.getStartMinute() * 60);
unsigned int stopseconds = (t.getStopHour() * 3600) + (t.getStopMinute() * 60);
int dayadjustment = -1;
if(weekday() == 1){
dayadjustment = 6; // needed for Sunday Time library is day 1 and Blynk is day 7
}
if(t.isWeekdaySelected((weekday() + dayadjustment))){ //Time library starts week on Sunday, Blynk on Monday
//Schedule is ACTIVE today
if(nowseconds >= startseconds - 31 && nowseconds <= startseconds + 31 ){ // 62s on 60s timer ensures 1 trigger command is sent
digitalWrite(signalPin, HIGH); // Tells SLAVE to ignore transmission
transmitter.deviceOn(TRANSMITTER_ID, 15); // Doesnt always work for some reason
Blynk.virtualWrite(V0, 1); // This however always work as long as it's connected to internet
Blynk.syncVirtual(V0);
Serial.println("Schedule 1 started");
terminal.println("Schedule 1 started");
terminal.flush();
timeStamp();
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW); // OK for SLAVE to receive again
}
if(nowseconds >= stopseconds - 31 && nowseconds <= stopseconds + 31 ){ // 62s on 60s timer ensures 1 trigger command is sent
digitalWrite(signalPin, HIGH);
transmitter.deviceOff(TRANSMITTER_ID, 15);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V0, 0);
Blynk.syncVirtual(V0);
Serial.println("Schedule 1 finished");
terminal.println("Schedule 1 finished");
terminal.flush();
timeStamp();
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW);
}
}
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V0) { // Unit (plug) 1
timeStamp(); // For debugging
digitalWrite(signalPin, HIGH); // Tells SLAVE to ignore transmission
if ( param.asInt() == 1 ) {
transmitter.deviceOn(TRANSMITTER_ID, 15);
Serial.println("RC 1 ON");
terminal.println("RC 1 ON");
terminal.flush();
}
else {
transmitter.deviceOff(TRANSMITTER_ID, 15);
Serial.println("RC 1 OFF");
terminal.println("RC 1 OFF");
terminal.flush();
}
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW); // OK for SLAVE to receive again
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V1) { // Unit 2
digitalWrite(signalPin, HIGH);
if ( param.asInt() == 1 ) {
transmitter.deviceOn(TRANSMITTER_ID, 14);
Serial.println("RC 2 ON");
terminal.println("RC 2 ON");
terminal.flush();
}
else {
transmitter.deviceOff(TRANSMITTER_ID, 14);
Serial.println("RC 2 OFF");
terminal.println("RC 2 OFF");
terminal.flush();
}
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW);
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V2) { // Unit 3
digitalWrite(signalPin, HIGH);
if ( param.asInt() == 1 ) {
transmitter.deviceOn(TRANSMITTER_ID, 13);
Serial.println("RC 3 ON");
terminal.println("RC 3 ON");
terminal.flush();
}
else {
transmitter.deviceOff(TRANSMITTER_ID, 13);
Serial.println("RC 3 OFF");
terminal.println("RC 3 OFF");
terminal.flush();
}
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW);
}
BLYNK_WRITE(V3) { // Group, all units
digitalWrite(signalPin, HIGH);
if ( param.asInt() == 1 ) {
transmitter.groupOn(TRANSMITTER_ID);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V0, 1);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 1);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, 1);
Serial.println("ALL IS ON");
terminal.println("ALL IS ON");
terminal.flush();
}
else {
transmitter.groupOff(TRANSMITTER_ID);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V0, 0);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, 0);
Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, 0);
Serial.println("ALL IS OFF");
terminal.println("ALL IS OFF");
terminal.flush();
}
digitalWrite(signalPin, LOW);
}
void reconnectBlynk() {
if (!Blynk.connected()) {
Serial.println("Lost connection");
if(Blynk.connect()) {
Serial.println("Reconnected");
}
else {
Serial.println("Not reconnected");
}
}
}
//============ Temperature sensor
/*
A note about about temperature readings from the DS18B20. The default resolution is 12 bits (0.0625 increments or 1/128 degrees C) and will take the sensor up to
750 ms to complete. This may seem like a problem, but it doesn't have to be (if I've done my homework correct)! startSensorConversation() tells the sensor(s) to start
the temp conversation which would normally make the program halt for ~750 ms. But by setting setWaitForConversion(0) to false, the request just initiate the conversation
and doesn't wait for it to finish. Total time for startSensorConversation() and getSensorData() functions is now a manageable 30-35 ms instead of 750-800! :)
The DS18B20 is rated for a minimum of 50.000 EEPROM Writes (but will probably do many many more). Even though it's a high number, getting a new reading once a minute
equals to 1440 a day, and after just 35 days your over 50.000! So to be a bit conservative, I now only do it once every 10 minute. I'm still running getSensorData()
once a minute so the data received is never older than 10 + 1 minute. That's OK for my needs.
*/
void startSensorConversation() {
DS18B20.requestTemperatures();
newTemp = true;
}
void getSensorData() {
if (newTemp) {
float temp = DS18B20.getTempCByIndex(0);
float roundedValue = ceilf(temp * 100) / 100; // well...
Serial.println(roundedValue);
Blynk.virtualWrite(5, roundedValue);
newTemp = false;
}
}
//============ Check serial buffer and parse data
void readSerialBuffer() {
if (newData == false) {
recvWithStartEndMarkers();
}
if (newData == true) {
strcpy(tempChars, receivedChars);
parseData();
//showParsedData(); // Debug only
newData = false;
}
}
//============ Read the serial buffer
void recvWithStartEndMarkers() {
static bool recvInProgress = false;
static byte ndx = 0;
char startMarker = '<';
char endMarker = '>';
char rc;
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
rc = Serial.read();
if (recvInProgress == true) {
if (rc != endMarker) {
receivedChars[ndx] = rc;
ndx++;
if (ndx >= numChars) {
ndx = numChars - 1;
}
}
else {
receivedChars[ndx] = '\0'; // terminate the string
recvInProgress = false;
ndx = 0;
newData = true;
}
}
else if (rc == startMarker) {
recvInProgress = true;
}
}
}
//============ Make use of the data received
void parseData() { // Split the data into its parts. Looks something like this <1912830,1,15,0,-1>
char * strtokIndx; // This is used by strtok() as an index
strtokIndx = strtok(tempChars,","); // The string
pTransmitter = atol(strtokIndx); // Transmitter ID
strtokIndx = strtok(NULL, ",");
pOn = atoi(strtokIndx); // ON or OFF (1 or 0)
strtokIndx = strtok(NULL, ",");
pChannel = atoi(strtokIndx); // Devcie number (13, 14, 15)
strtokIndx = strtok(NULL, ",");
pGroup = atoi(strtokIndx); // Group ON or OFF (1 or 0)
strtokIndx = strtok(NULL, ",");
pDim = atoi(strtokIndx); // Dim values
if (pChannel == 15 && pGroup == 0){ // Unit 1, NOTICE: Group also has 15
Blynk.virtualWrite(V0, pOn);
Blynk.syncVirtual(V0);
}
else if (pChannel == 14) { // Unit 2
Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, pOn);
Blynk.syncVirtual(V1);
}
else if (pChannel == 13) { // Unit 3
Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, pOn);
Blynk.syncVirtual(V2);
}
else if (pChannel == 15 && pGroup == 1) { // Group
Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, pOn);
Blynk.syncVirtual(V3);
}
}
//============ Main LOOP
void loop() {
if(Blynk.connected()) {
Blynk.run();
}
timer.run();
}
//============ Print parsed data to serial, only used when debugging
/*
void showParsedData() {
Serial.print("Transmitter ");
Serial.println(pTransmitter);
Serial.print("on ");
Serial.println(pOn);
Serial.print("channel ");
Serial.println(pChannel);
Serial.print("group ");
Serial.println(pGroup);
Serial.print("dim ");
Serial.println(pDim);
}
*/
Code for SLAVE:
/**
RF433_Slave.ino
Used togheter with RF433_Master.ino
Dont forget common ground!
**/
#include "NexaSelfLearningReceiver.h"
const byte GND = 2; // Receiver plugged directly to the board
const byte VCC = 5; // "
uint8_t RX_PIN = 3; // Could be 4
uint8_t RX_LED = 13; // Built in LED
// SLAVE Serial TX pin 1 is connected to MASTER RX pin 0
const byte signalPin = 12; // From: MASTER pin 9. If HIGH, don't decode (= Master is sending)
const byte piezoPin = 8; // Make some Noice (Yes, phun intended! Noice is a Swedish late 70-80 punk rock group ;) )
//============ Receiver
uint32_t hardCodedRC = 1912830; // My remote controlers hardcoded ID.
NexaSelfLearningReceiver receiver = NexaSelfLearningReceiver(RX_PIN, RX_LED);
uint32_t transmitter = 0;
bool on = false;
bool group = false;
uint8_t channel = 0;
short dim = 0;
uint64_t receivedSignal = 0;
//============ Piezo
unsigned int highHz = 2000; // Hz
unsigned int lowHz = 1700; // Hz
unsigned long duration = 30; // milliseconds
//============ Setup
void setup(){
pinMode(signalPin, INPUT); //
pinMode(GND, OUTPUT); // Give Rx GND and VCC
pinMode(VCC, OUTPUT); // "
digitalWrite(GND, LOW); // "
digitalWrite(VCC, HIGH); // "
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("In the beginning ..");
tone(piezoPin, highHz, duration);
};
//============ Main LOOP
void loop() {
receivedSignal = receiver.receiveSignal(&transmitter, &on, &group, &channel, &dim, 1000);
// Stop receiving when transmitter is sending to avoid disco
if (digitalRead(signalPin) == LOW) {
// Just want my own remote
if(receivedSignal != 0 && transmitter == hardCodedRC) {
Serial.print("<"); // startMarker
Serial.print(transmitter);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(on);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(channel);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(group);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(dim);
Serial.print(">"); // endMarker
Serial.println("");
// Make a short beep so I know it received and decoded the signal. High pitch = ON, low = OFF
if (on) {
tone(piezoPin, highHz, duration);
}
else {
tone(piezoPin, lowHz, duration);
}
}
}
}
Feedback, suggestions, improvements and cookies are most welcome!